Grade 6 Foundation
March 19, 2025 2025-07-29 15:54Grade 6 Foundation
Course Description
The Grade 6 Foundation Course is designed to provide students with a broad academic base across Mathematics, Science, and Logical Reasoning. The curriculum introduces students to essential mathematical concepts like number systems, algebra, geometry, data handling, and ratios while laying the groundwork for problem-solving and analytical thinking. In Science, students explore key ideas in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, including matter and its properties, energy transformations, electricity, human anatomy, plant systems, and ecosystems. Logical Reasoning topics enhance their pattern recognition and critical thinking abilities. The course ensures a gradual progression from fundamental ideas to more structured applications, preparing students for advanced academic challenges.
Learning Objective
This course aims to develop computational fluency and logical reasoning by strengthening number sense, operations, and foundational algebraic skills. Students will gain the ability to visualize and solve geometrical problems and interpret statistical data meaningfully. In Science, the objective is to build an intuitive understanding of physical quantities, forces, energy, properties of matter, and the basics of life processes. Students will also develop the ability to approach real-world situations with scientific temper and critical analysis. Throughout the course, emphasis is placed on fostering curiosity, precision in scientific thought, and a structured approach to problem-solving, equipping students with skills essential for higher studies and competitive environments.
What Will I Learn?
Students will learn to work confidently with numbers, fractions, decimals, percentages, and basic algebra. They will understand shapes, areas, volumes, and angles in geometry, and develop data interpretation skills through statistics and logical reasoning. In science, they will explore the fundamentals of matter, atoms, mixtures, motion, energy, electricity, magnetism, and light. They will also study the basics of human body systems, nutrition, microorganisms, ecosystems, and environmental balance. Throughout the course, students will build strong analytical skills, scientific thinking, and a foundation for higher studies.
Additional Info
Practice
Regular exercises and interactive activities to reinforce key concepts in each subject.

Doubt-Solving
Dedicated sessions to address and clarify any questions or difficulties students encounter.
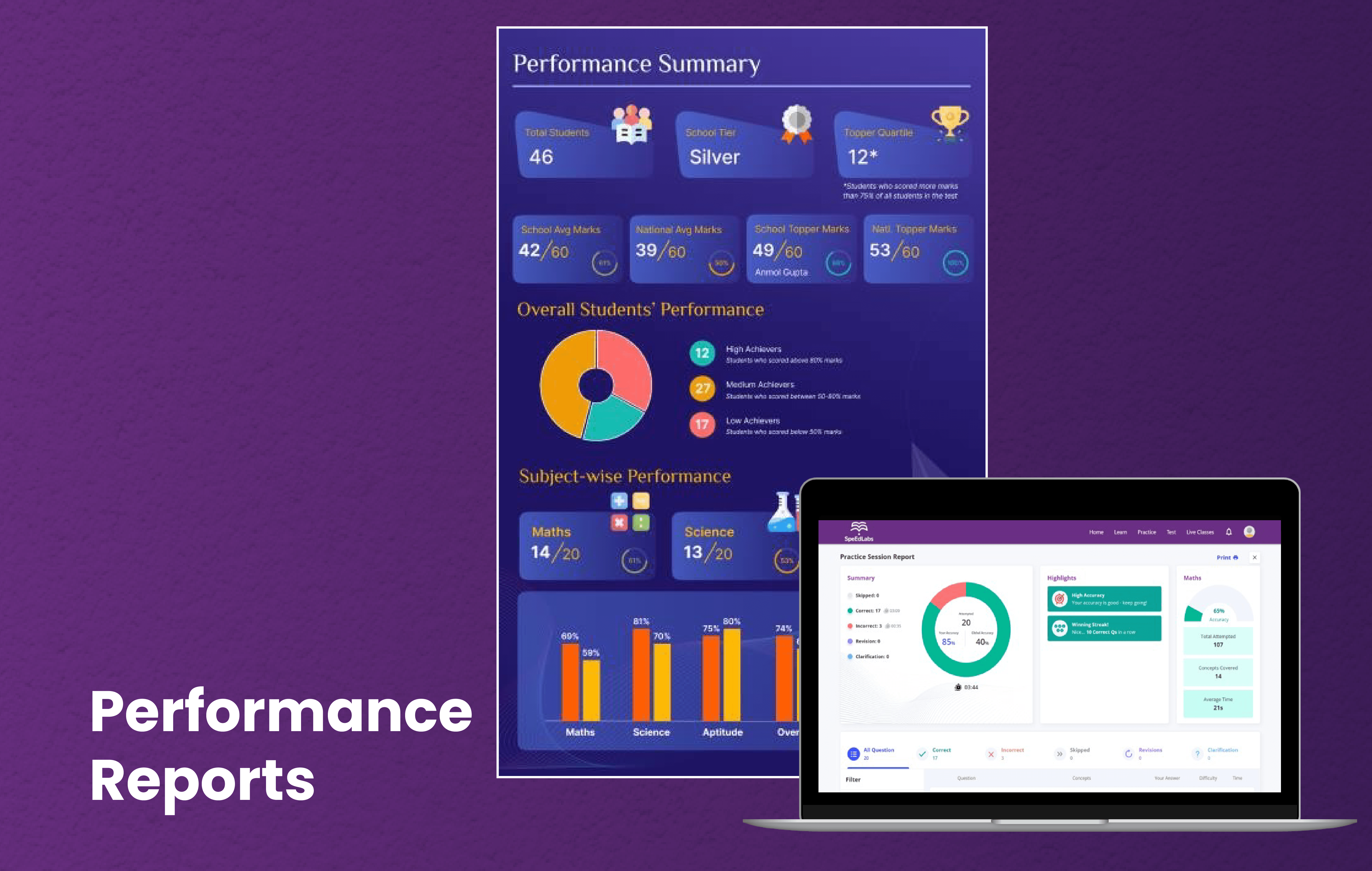
Reports
Detailed reports on experiments and projects to track progress and understanding.
Showing search results
Mathematics
Chemistry
Physics
Biology
Number System
Introduction to Numbers
Predecessor and Successor
Factors and Multiple
Types of Numbers
Tests of Divisibility (I)
Tests of Divisibility (II)
Prime Factorisation, Common Factors and Common Multiple
Highest Common Factor
LCM
Properties of HCF and LCM, Some Real-Life Problems in HCF and LCM, Relationship between LCM and HCF
Integers, Number Line
Addition and Subtraction of Integers
Multiplication and Division of Integers
Properties of Integers
Additive identity, Additive inverse
Fractions and Decimals
Introduction to Fractions, Representation of Fractions on Number Line, Types of Fractions
Equivalent Fractions, Simplest form of Fractions, Comparison of Fractions
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
Multiplication of Fractions, Reciprocal of Fractions
Division of Fractions, Rational Numbers
Equivalent Rational Numbers, Simplest (Lowest) or Standard Form of a Rational Number
Equality of Rational Numbers, Comparison of Rational Numbers
Decimal Numbers
Decimal Places, Rounding with Decimal Numbers
Types of Decimals, Conversion of Fraction to Decimals and Vice-versa
Comparison of Decimals
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
Multiplication of Decimals
Division of Decimals
Percentage and its Applications
Percentage
Expressing Percentage as a Fraction or Decimal
Converting Fractional Numbers and Decimals to Percentages
Comparison of Percentages
Increase or Decrease as Percentage
Applications of Percentage (I)
Applications of Percentage (II)
Exponents and Powers
Introduction to Exponents
Laws of Exponents (I and II)
Laws of Exponents (III and IV)
Laws of Exponents (V and VI)
Use of Exponents in Expressing Large Numbers
Standard form
Set Theory
Introduction of Sets
Some sets of numbers and their notations
Representation of Sets
Types of Sets (I)
Types of Sets (II)
Operation on Sets
Venn Diagram (I)
Venn Diagram (II)
Some Formulae on the Cardinality of Sets
Basic Geometry
Introduction to Geometry, Basic Terms, Pair of Lines
Curves and Types of Curves, Curves Around Us and Position in a Curve, Angles, Interior, Exterior and Boundary of an Angle
Polygons, Sides, Vertices and Diagonals, Types of Polygon
Triangles and Types of Triangles, Angle Sum Property
Exterior Angle Property of a Triangle
Quadrilaterals, Classification of Quadrilaterals, Counting polygons in given figures
Circles, Introduction to Coordinates and its Elements
Quadrant, Convention of Signs
Locating a Point on the Coordinate Plane, Point on the Axes
Lines and Angles
Introduction, Basic Terminologies, Angles
Types of Angles
Pair of Angles
Pair of Lines, Angles formed by a Transversal
Corresponding angles
Alternate angles
Co-interior angles
Check for Parallel Lines
Algebraic Expressions
Introduction (Variables, Constants, Terms, Coefficient)
Types of Terms
Types of Algebraic Expressions
Addition and Subtraction of Algebraic Expressions
Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions
Division of Algebraic Expressions
Finding the Value of an Expression
Polynomial and Types of Polynomial
Linear Equations in One Variable
Introduction to Equations, Linear Equation, Simple Equation
Properties of an Equation
Methods of Solving Simple Equation
Solving Equations having the variable on one side
Solving Equations having the variable on both sides
Applications of Linear Equations (I)
Applications of Linear Equations (II)
Ratio and Proportion
Introduction to Ratios, Simplest Form of a Ratio
Equivalent Ratios
Comparison of Ratios
Dividing Some Quantity in the Given Ratio, Properties of a Ratio
Difference between a Fraction and a Ratio, Ratio into Fraction and Percentage
Proportion, Direct and Inverse Proportions
Direct and Inverse Proportions Problems
Unitary Method, Applications of Unitary Method
Perimeter and Area
Plane Figures, Polygon, Perimeter
Perimeter of Rectangle and Square
Perimeter of Regular Shapes
Types of Triangles, Perimeter
Area of Triangles
Area of Rectangle and Square
Area of Rectangle and Square (Word Problem)
Perimeter and Area of Parallelogram
Perimeter and Area of Trapezium
Circle, Perimeter of Circle
Area of Circle
Surface Area and Volume
Introduction to Surface Area
Surface Area of Cube (TSA + LSA)
Surface Area of Cuboid (TSA + LSA)
Surface Area of Cylinder (TSA + LSA)
Introduction to Volume
Volume of Cube
Volume of Cuboid
Volume of Cylinder
Statistics
Recording or Collection of Data and Types of Data
Organisation of Data and Types of Graphs
Pictograph, Drawing a Pictograph, Interpretation of a Pictograph
Bar Graph and Interpretation of a Bar Graph
Drawing a Bar Graph
Double Bar Graph
Histogram
Introduction to Mean, Mode
Median
Logical Reasoning
Series Completion (I)
Series Completion (II)
Series Completion (III)
Inserting the Missing Character (I)
Inserting the Missing Character (II)
Mirror and Water Images (I)
Mirror and Water Images (II)
Mirror and Water Images (III)
Distance and Direction (I)
Distance and Direction (II)
Symbols and Formulae
Introduction
Symbols, Significance of a Symbol
Elements
Characteristics of an Element, Symbols of Elements
Elements are made up of Atoms
Valency
Formula of the Compound
Chemical Formulae
Writing the Formula of the Compound, Criss-Cross Method
Study of Materials
Introduction, Object
Grouping and its Importance
Classification of Objects (Materials, Natural and Man-Made Materials)
Matter and its States (Solid, Liquid and Gases), Interconversion of States of Matter
Properties of Materials (Appearance, Metals and their Properties)
Non-metals and their Properties, Hardness, Texture
Transparency, Solubility, Sinking and Floating
Separation of Substances
Introduction and Classification of Substances
Pure Substances
Types of Mixtures
Methods of Separation (Threshing, Winnowing, Handpicking, Sieving, Magnetic Separation)
Methods of Separation (Sedimentation, Decantation and Filtration, Distillation, Chromatography)
Sublimation, Use of More than One Method of Separation
Solubility and Water (A Universal Solvent)
Introduction to Chemistry
Introduction (Development of Chemistry)
Branches of Chemistry
Applications of Chemistry
An Historical Viewpoint
Chemistry in Various Aspects (Food and Chemistry, Cosmetics and Chemistry, Clothing and Chemistry)
Chemistry in Various Aspects (Medicine and Chemistry, Industries and Chemistry, Chemistry and Energy Resources)
Dark Side of Chemistry
States of Matter
Elements and Compounds
Modern Concept of an Atom
Pure Substance, Mixture
Great Chemists and Their Contributions
Four Chemistry Inventions of Modern World
Basics of Chemistry
Introduction, Importance of Physical Chemistry
Applications of Physical Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry (Classification of Inorganic Chemistry)
Acids (Properties and Examples)
Bases (Properties and Examples)
Salts (Characteristics and Common Examples)
Organic Chemistry (Importance and Some Common Examples)
Important Block Elements
Introduction
Elements and Their Classification
Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids
Compounds and Mixtures
Some Common Elements (Lithium, Beryllium)
Some Common Elements (Boron, Carbon)
Some Common Elements (Nitrogen, Oxygen)
Some Common Elements (Fluorine, Neon)
Fundamentals of Elements
Introduction, Classification of Matter
Atoms, Molecules, Types of Molecules
Elements
Classification of Elements (Metals, Physical Properties and Applications)
Non-Metals (Properties and Applications)
Metalloids
Some Common Elements (Sodium, Magnesium)
Some Common Elements (Aluminium, Silicon)
Some Common Elements (Phosphorus, Sulphur)
Some Common Elements (Chlorine, Argon)
Introduction to Measurement
Introduction to Measurement (Physical Quantity, Standard Unit and Types of Units)
System of Units
Measurement (Measurement of Length)
Measurement of Mass and Weight
Measurement of Time
Area and Measurement of Area
Volume and Measurement of Volume (Some Common Practical Units)
Basic Maths and Vectors
Introduction to Exponents and Powers
Angles, Triangles and Trigonometry
Physical Quantities, Representation of Vectors, Angle between Vectors
Types of Vectors, Magnitude of Vector
Calculation of Unit Vector, Addition of Vectors
Motion
Physical Quantities, Introduction to Rest and Motion
Types of Motion
Distance, Displacement
Speed and its Types
Velocity and its Types
Acceleration and its Types
Equations of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion
Force and Effects of Force
Non-Contact Forces
Contact Forces, Net Force, Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
Inertia and its Types, Newton's First Law of Motion
Momentum, Newton's Second Law of Motion, Newton's Third Law of Motion
Work, Energy and Power
Introduction to Work (Types of Work, Units of Work)
Energy (Types of Energy - Mechanical Energy)
Types of Energy (Heat, Solar, Electrical, Magnetic, Light, Sound Energy)
Energy Transformation, Law of Conservation of Energy
Sources of Energy, Energy Chains
Work-Energy, Power
Electricity and Magnetism
Types of Electricity, Generation of Electricity, Sources of Electricity
Electric Charge, Electric Current
Electric Circuit, Types of Electric Circuit
Electric Cell and Battery (Different Types of Cells, Dry Cell)
Electricity from Wind and Water, Effects of Electricity
Introduction to Magnets, Magnets of Different Shapes, Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
Poles of a Bar Magnet, Properties of Magnets, Action of Magnets
Magnetic Compass, Magnetic Field and Field Lines
Magnetic Flux, Earth as a Magnet
Light and Spectrum
Light and its Properties (Sources of Light, Ray and Beam of Light)
Sources of Light, Rectilinear Propagation of Light, Transparent, Translucent and Opaque Objects
Reflection of Light, Refraction of Light
Shadows and its Formation
Eclipse
Terms Used to Represent Wave Nature of Light
Colours in White Light and their Frequency and Wavelength Range, Dispersion of Light
Deviation Produced by Prism, Electromagnetic Spectrum
Properties and Uses of Different Radiations of Electromagnetic Spectrum
The Living World
Introduction, Interplay of Living and Non-living Things, Characteristics of Living Things (Level of Organization)
Characteristics of Living Things (Movement, Growth and Nutrition)
Characteristics of Living Things (Respiration and Metabolism)
Characteristics of Living Things (Excretion and Responsiveness)
Characteristics of Living Things (Reproduction, Lifecycle), Characteristics of Non-Living Things
Differences between Living and Non-Living Things, Plant Life Cycle
Microscope
Microorganisms
Nutrients: The Chemical Compounds of Food
Introduction, Nutrients of Food (Carbohydrates, Fats and Proteins)
Nutrients of Food (Vitamins and Minerals, Water and Roughages)
Biochemical Test for Detection of Carbohydrates, Proteins and Fats, Diet
Millets and Loss of Nutrients in Food
Deficiency Disease, Vitamins and Minerals Deficiency
Carbohydrate Deficiency and Protein Deficiency
The Amazing Journey of Food
Adolescence and Chemical Coordination in Animals
Introduction and Puberty
Changes that Mark Adolescence (Growth Spurt, Changes in Body Shape and Voice)
Reproductive Phase in Humans, Adolescence (Changes in Behaviour)
Endocrine System
Adolescence and Health
Organ Systems of Human Body
Introduction, Digestive System
Respiratory System
Circulatory System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Excretory System
Morphology of Flowering Plants
Introduction, Classification of Plants (Based on Flowers, Lifespan and Nature of Stem)
Classification of Plants (Based on Habitat), Plant System (Root System, Regions of Root)
Types of Root System, Functions and Modifications of Roots
Shoot System, Stem, Functions of Stem, Stem Modifications
Leaf, Types of Venation, Types of Leaf
Functions of Leaf, Leaf Modifications, Phyllotaxy
Flower, Types of Flower
Pollination, Fertilization, Fruit, Seed and Types of Seed
Movement in Animals and Plants
Movement and Locomotion, Joints and Its Types (Ball and Socket, Hinge, Pivot and Gliding Joint)
Movable Joints (Saddle and Ellipsoid Joint), Bones, Human Skeleton and Its Functions
Human Skeleton (Axial Skeleton System)
Appendicular Skeleton
Cartilage and Muscles
Locomotion and Movement in Other Animals
Movement in Plants
Ecosystem
Introduction, Ecosystem and Its Classification
Components and Functions of Ecosystem
Food Chain
Food Web and Biomagnification
Ecological Pyramids
No results found matching your query.
Loading PDF access status...
Loading PDF access status...
Loading PDF access status...
Loading PDF access status...
×
Access All Study Materials
Please fill in your details below to access all study materials for this course.

Subjects Includes
 Math
Math Physics
Physics Chemistry
Chemistry Biology
Biology